PSD2 (Payment Service Directive (derived)) is an EU law which regulates access to your financial data by organisations other than your bank.
It is critical to the growth of Open Banking within the EU as it mandates banks to make their customers financial data available via APIs to registered third party vendors.
What is the purpose of PSD2?
The purpose of PSD2 is to:
- Encourage innovation and competition in retail payments
- Improved security for payment transactions
- Protect customer data.
How does PSD2 work?
Basically Open Banking lets approved companies access bank accounts with the account holders’ permission.
Third party financial service providers need an account information service provider (AISP) license and/or a payment initiation service provider (PISP) license before they can offer Open Banking Services.
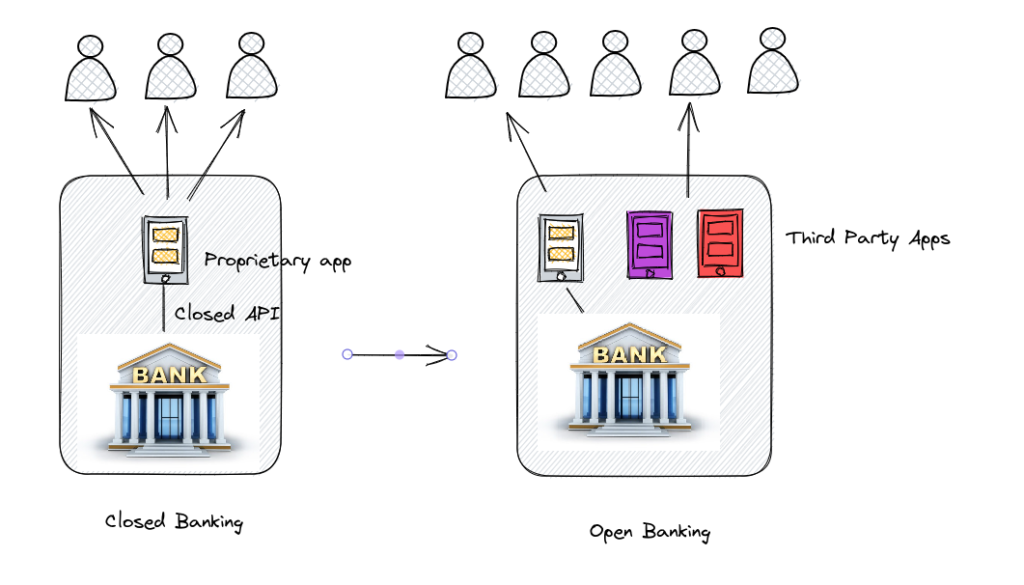
PSD2 facilitates the migration of banking applications to an open innovative ecosystem.
Technical Terms
PSD2 introduces a number of technical terms. The diagram below shows where these terms are applicable within Open Banking
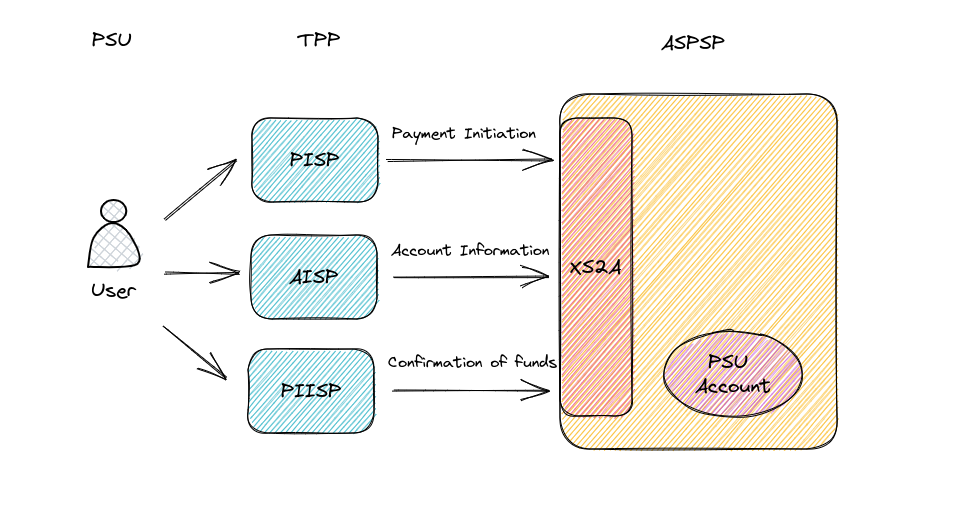
PISP – Payment Information Service Provider. Third Party PISPs can initiate payments directly from customers payments account assuming they have the customers consent.
AISP – Account Information Service Provider. AISPs can access a customers data from different banks to give an overall overview of their financial position.
TPP – Third Party Payment Service Providers
PSU – Payment Service Users
ASPSP – Account Servicing Payments Service Provider. Financial institution holding a customer account, i.e. Bank.
XS2A – Access to account
PSD2 Services
PSD2 regulates two popular services available already:
- Payment Initiation Services (PIS)
- Account Information Services (AIS).
PIS allow customers to make online purchases without a credit card. This means that you can use a bank transfer to make a purchase without any delay.
AIS allows the collection of a customers financial information from different bank accounts into one location.