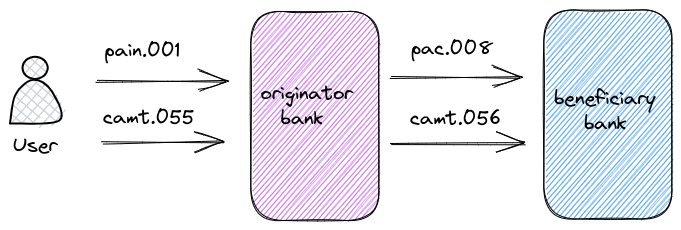
The ISO 20022 Camt.054 is a notification message sent by the originator bank to the originator informing them of a credit(s) or debit(s) against their account. It does not contain balance information.
Even though, the Camt.054 is part of the ISO20022 standard, it is optional. A bank can choose whether to send it or not.
The definition of the Camt.054, along with its message definition reports, can be found here.
Building blocks of Camt.054
Camt.054 contains two blocks:
Group Header
Contains identifying information for all of the debits/credits in the message. The Group Header may also contain:
- message id – used to identify each message.
- creation date and time – indicates when the payments(s) referenced were created.
- number of transactions – count of the number of transactions in the message
- control sum – contains a sum of the total number of transactions in the message
- initiating party – contains information on the party who initiated the payment.
Ntfctn
Contains information about the transactions in the message. The ntfctn may also contain:
- Notification Message Identification – contains a unique id used to identify each notification in the message
- Notification Date – notification creation date.
- Additional Notification Information – used to provide additional information about the notification.
- Notification Message Name Identification – code indicating the category of notification message.