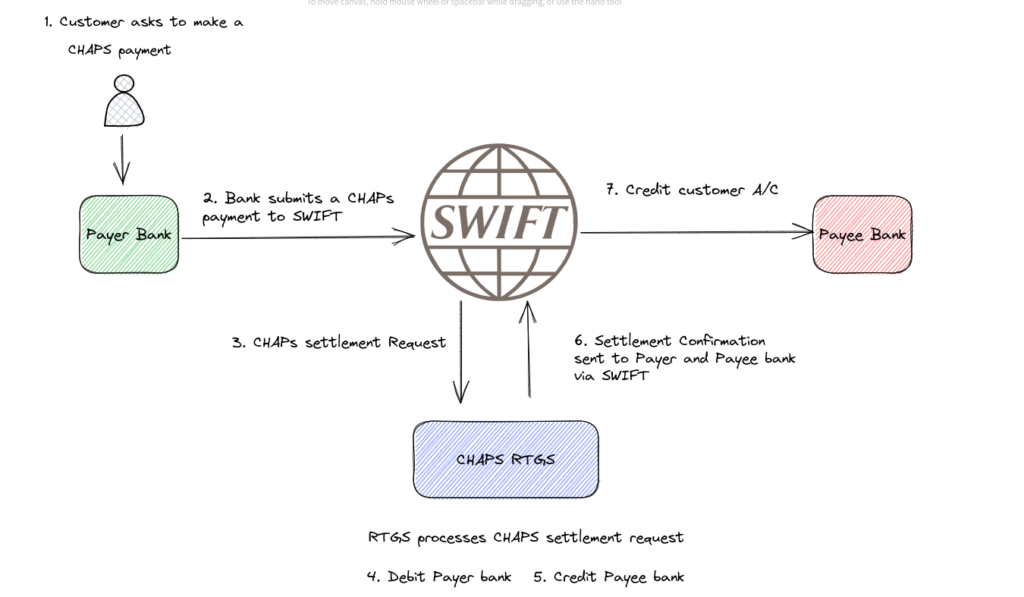
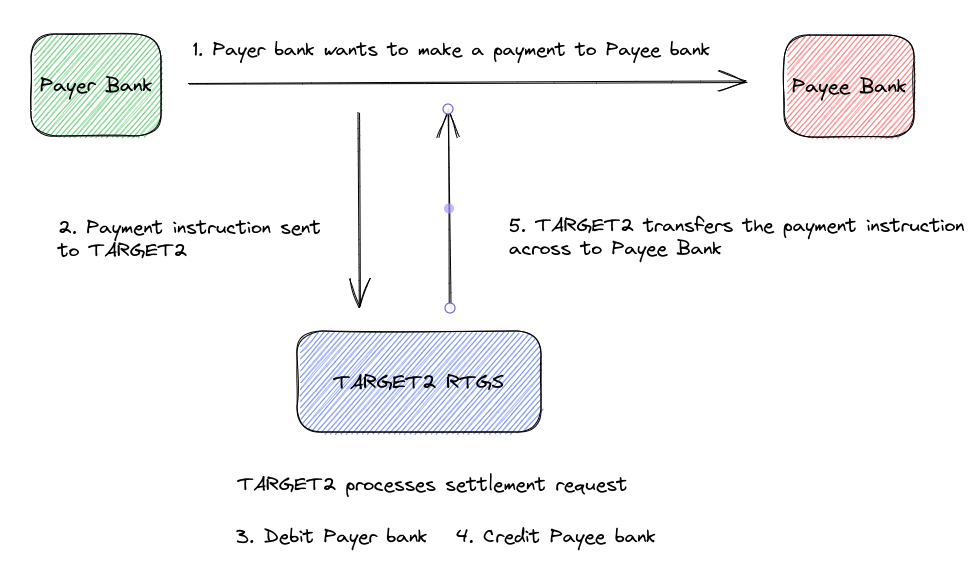
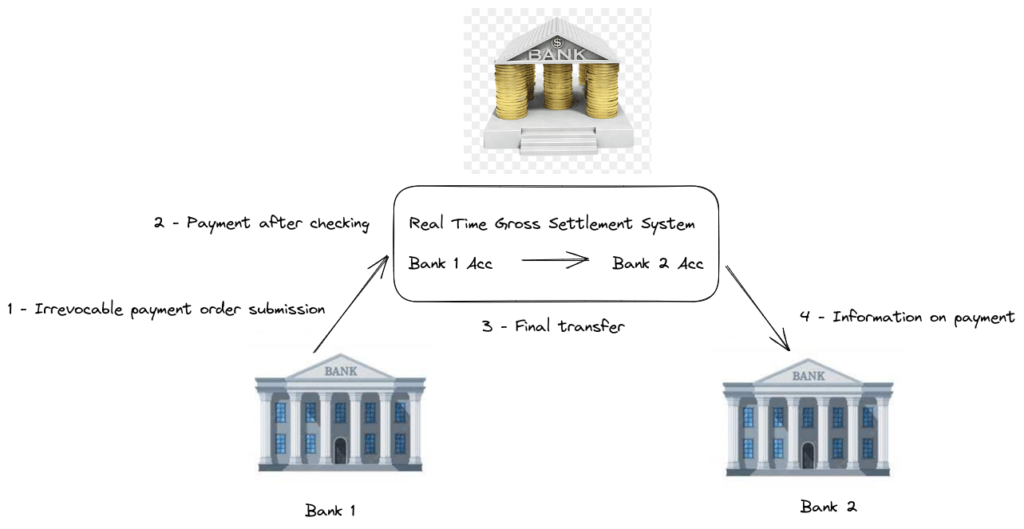
(Real-Time) Gross Settlement (RTGS) are settlement systems that facilitate the transfer of funds instantly. They are used for inter-bank high-value payments that needed to be cleared immediately.
Examples of RTGS settlement systems are TARGET2, used in the Eurozone area, FedWire Funds Service, used in the United States and CHAPs, used in the UK. RTGS systems are run by central banks, i.e. CHAPS is run by Bank of England, Target2 by the European Central Bank and FedWire by the Federal Reserve.

An RTGS transaction means that:
- Each transaction gets settled in real-time by the central bank. An RTGS transaction is not subject to any wait time.
- Gross settlement means that the transaction is settled on a one-to-one basis and is not bundled with any other transactions.
Advantages of an (Real-Time) Gross Settlement (RTGS)
- Accurate Cash Flow – As an RTGS transaction is settled immediately, customers know when exactly their accounts are debited/credited, thereby ensuring more predictable cash flows.
- Reduced risk – RTGS transactions are settled immediately meaning that there is less risk for the receiving party. Funds will already have been credited to the receiving party by the time the payment instruction arrives.