
Nacha govern the ACH (Automated Clearing House) payments network in United States. It stands for National Automated Clearing House Association.
It also manages the Operating Rules for ACH Payments. These define the rules and responsibility of any participants using the ACH network. However, the ACH operators, Federal Reserve, and the Electronic Payment Network run the ACH network, not Nacha.
Some of Nacha’s responsibilities are:
- Promote the ACH network
- Enforcing the rules governing the ACH network
- Steering the evolution of the ACH network in the evolving payments world
What are the Nacha operating rules?
Each participant of the ACH network must adhere to rules if it wants to accept ACH payments. These rules are broad and participants of the ACH network need to stay up to date to ensure compliance. Participants can be fined or removed from the ACH network in the event of non-compliance. You can obtain a copy of the rules here.
Examples of Nacha operating rules
The following are examples of Nacha operating rules around ACH direct debit
- Ensure customer information such as bank account numbers, social security numbers, billing addresses are secure.
- Customers must clearly authorise any ACH direct debits.
- Any change to amount of the ACH direct debits needs to be communicted clearly to the customer
- Cancelled ACH direct debits need to be completed in a timely manner.
What is Nacha file format?
A Nacha file is a set of ACH instructions used to initiate a payment over the ACH network. A record (line) in a Nacha file must be 94 characters in length.
Fields that begin and end at certain positions make up each record. These fields contains important information such as account number and routing number. Additionally each record must follow a certain order.
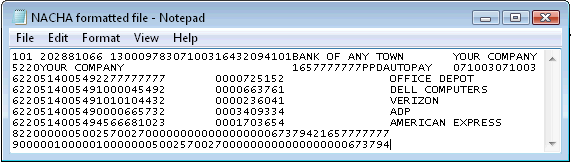
Although banks mostly use Nacha files for payment initiation, they can also use the file format for a wide variety of other purposes such as reversals or returns.